The solid modeling method is typically used when modeling with solid features. The following are key features of the solid modeling approach:
It is characterized by 2D sketches/profiles used in creating extrusions, revolutions, and lofts to form solids, and blends on the edges of solids.
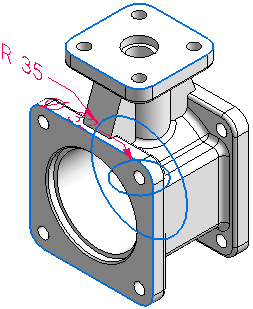
It most often involves the addition or subtraction of material using analytic shapes.
The model's topology is driven by faces.
Holes are used for alignment.
Feature faces are used for alignment as well as for mating with other features.
Edges are rounded for safety and strength.
Edges and faces are primarily analytic-based.
Modeling with surface-based features typically begins with a wireframe, from which surfaces are generated. Key features of surface modeling:
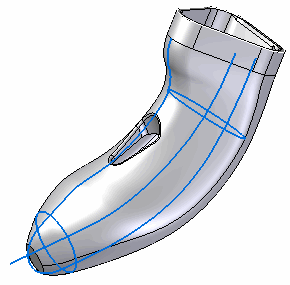
It is characterized by control points used to define 2D and 3D curves.
A model's topology is driven by edges and curves. Edges and faces are mainly based on splines.
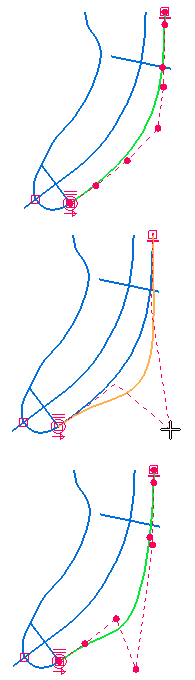
Surface shapes are very important, therefore direct editability of underlying curves and edges is crucial.
Highlight lines, silhouette edges and flow lines of a model are important.