Applies a path relationship between two parts in an assembly. You use a path relationship to define how one part will move relative to another part along a path. Like the Cam relationship, the path relationship requires a follower and a chain as input. The centerline of a slot feature can be used as input for the path relationship. See the help topic Slot command.
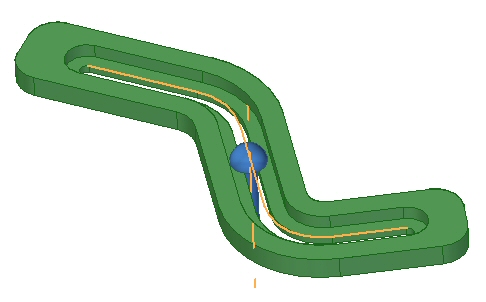
In the image above, two relationships keep the pin in the slot. A mate relationship keeps the flat face of the pin in the recessed slot and the path relationship intersects and aligns the cylindrical axis of the pin with the slot path. To have a valid slot path, the slot must have been created with the slot command in the part environment.
Note:
The path relationship can be used to define a range of motion for a component and can be used as an alternative to the range offset used when creating other relationships. Using the path relationship for this purpose provides a more efficient processing method than using a range offset.
Note:
The edge chain can be defined from part geometry or sketch elements included assembly sketches.
If the input chain is not tangent continuous, small fillets are added to non-tangent corners when the path is defined for processing.
The chain does not have to be planar. 3D paths are valid.
Open and closed chains are valid.
The chain can not self intersect.